The Hsieh Lab



The Hsieh Lab

Selective Publications
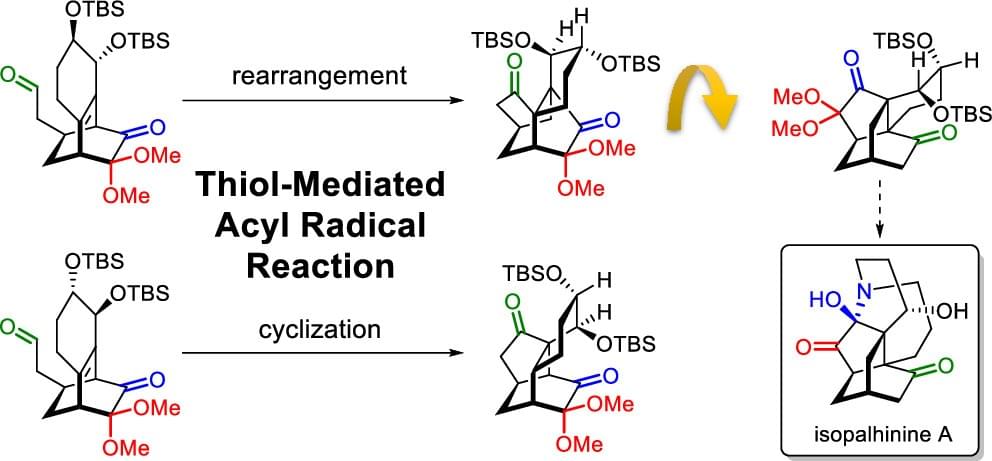
Noncovalent Interaction Effects on the Acyl Radical Reaction of Bicyclo[2.2.2]octanone: Selective Formation of Rearrangement and Cyclization Products
Org. Lett. 2025, 27, 8394–8398.
The influence of allylic substituent orientation on the six-membered fused ring, as well as the steric hindrance at the alkene bridge (R1 and R2) and bridgehead (R3), on the thiol-mediated acyl radical rearrangement/cyclization of bicyclo[2.2.2]octenone was investigated. A combined analysis using density functional theory calculations and interaction region indicator analysis suggests that reaction selectivity is driven by functional group noncovalent interactions.
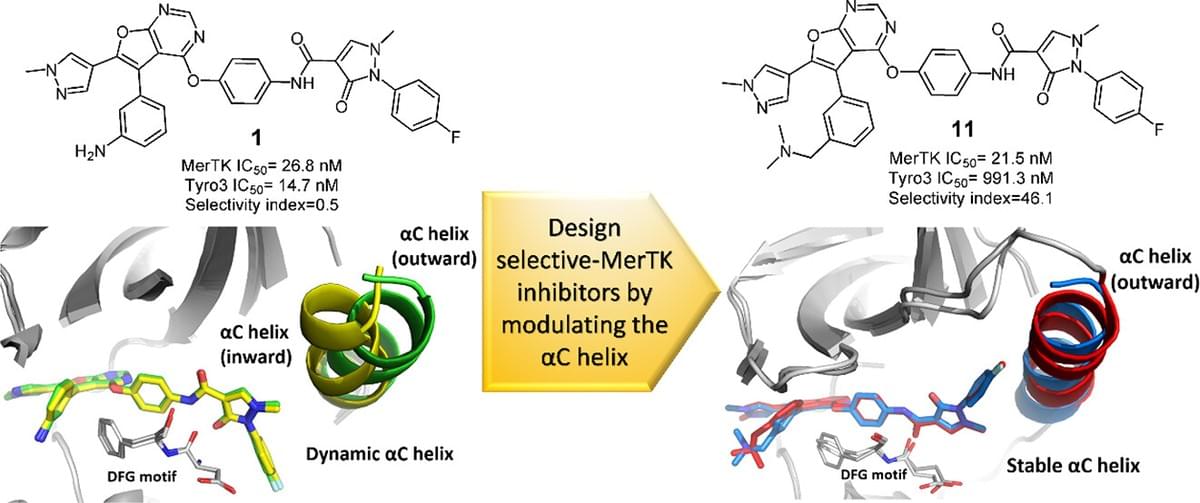
Structure-Based Design of Potent and Selective MerTK Inhibitors by Modulating the Conformation of αC Helix
Tumor-associated macrophages play an important role in cancer progression and immunosuppression, making their receptors promising therapeutic targets. MerTK, a TAM receptor, regulates macrophage efferocytosis and polarization, and its inhibition holds potential for tumor growth suppression and immune modulation. However, Tyro3, another TAM receptor, is involved in neurogenesis, highlighting the need to selectively target MerTK while avoiding Tyro3 inhibition to prevent neurotoxicity. In this study, we present a novel strategy for designing MerTK-selective inhibitors by modulating the conformational dynamics of its αC helix. By integrating structural biology, medicinal chemistry, protein stabilization assays, and molecular docking studies, we identified compound 11, which demonstrates potent inhibition and selectivity for MerTK. Pharmacokinetic evaluations and in vivo studies further reveal compound 11 as a promising candidate for further development. Our findings not only advance the understanding of the MerTK-specific mechanism but also propose a strategy for designing selective kinase inhibitors targeting the αC helix conformation.
Novel Naphthyridones Targeting Pannexin 1 for Colitis Management
Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2411538.
Pannexin 1 (PANX1) forms cell-surface channels capable of releasing signaling metabolites for diverse patho-physiological processes. While inhibiting dysregulated PANX1 has been proposed as a therapeutic strategy for many pathological conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), low efficacy, or poor specificity of classical PANX1 inhibitors introduces uncertainty for their applications in basic and translational research. Here, hit-to-lead optimization is performed and a naphthyridone, compound 12, is identified as a new PANX1 inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.73 µm that does not affect pannexin-homologous LRRC8/SWELL1 channels. Using structure-activity relationship analysis, mutagenesis, cell thermal shift assays, and molecular docking, it is revealed that compound 12 directly engages PANX1 Trp74 residue. Using a dextran sodium sulfate mouse model of IBD, it is found that compound 12 markedly reduced colitis severity, highlighting new PANX1 inhibitors as a proof-of-concept treatment for IBD. These data describe the mechanism of action for a new PANX1 inhibitor, uncover the binding site for future drug design, and present a targeted strategy for treating IBD.
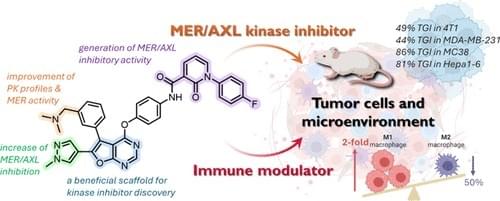
Discovery of Dual MER/AXL Kinase Inhibitors as Bifunctional Small Molecules for Inhibiting Tumor Growth and Enhancing Tumor Immune Microenvironment
J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 10906–10927.
A series of bifunctional compounds have been discovered for their dual functionality as MER/AXL inhibitors and immune modulators. The furanopyrimidine scaffold, renowned for its suitability in kinase inhibitor discovery, offers at least three distinct pharmacophore access points. Insights from molecular modeling studies guided hit-to-lead optimization, which revealed that the 1,3-diketone side chain hybridized with furanopyrimidine scaffold that respectively combined amino-type substituent and 1H-pyrazol-4-yl substituent on the top and bottom of the aryl regions to produce 22 and 33, exhibiting potent antitumor activities in various syngeneic and xenograft models. More importantly, 33 demonstrated remarkable immune-modulating activity by upregulating the expression of total T-cells, cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells, and helper CD4+ T-cells in the spleen. These findings underscored the bifunctional capabilities of 33 (BPR5K230) with excellent oral bioavailability (F = 54.6%), inhibiting both MER and AXL while modulating the tumor microenvironment and highlighting its diverse applicability for further studies to advance its therapeutic potential.
Influence of Ring Strain on the Formation of Rearrangement vs Cyclization Isotwistane Products in the Acyl Radical Reaction of Bicyclo[2.2.2]octanone
Org. Lett. 2023
An acyl radical reaction of bicyclo[2.2.2]octenone to yield either rearranged or cyclized isotwistane products is described. The influence of ring strain on the reaction was demonstrated by alternating the sizes of the fused ring in the starting material. DFT calculations showed that the reaction is under thermodynamic control and proceeds via a 5-exo-trig cyclization intermediate, which undergoes either hydrogen-atom transfer (HAT) to give a cyclized product or rearrangement via a twistane intermediate to give a rearranged product
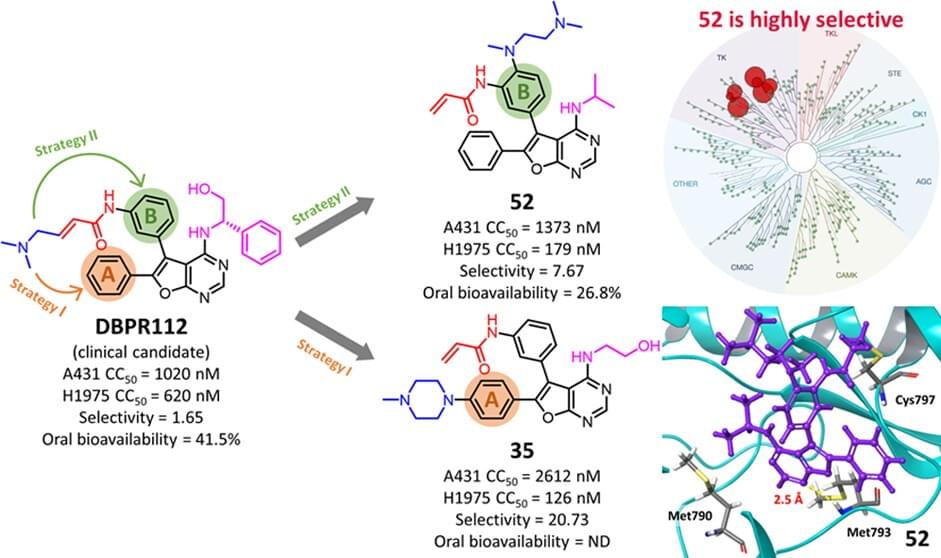
Development of Furanopyrimidine-Based Orally Active Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 2566–2588
The development of orally bioavailable, furanopyrimidine-based double-mutant (L858R/T790M) EGFR inhibitors is described. First, selectivity for mutant EGFR was accomplished by replacing the (S)-2-phenylglycinol moiety of 12 with either an ethanol or an alkyl substituent. Then, the cellular potency and physicochemical properties were optimized through insights from molecular modeling studies by implanting various solubilizing groups in phenyl rings A and B. Optimized lead 52 shows 8-fold selective inhibition of H1975 (EGFRL858R/T790M overexpressing) cancer cells over A431 (EGFRWT overexpressing) cancer cells; western blot analysis further confirmed EGFR mutant-selective target modulation inside the cancer cells by 52. Notably, 52 displayed in vivo antitumor effects in two different mouse xenograft models (BaF3 transfected with mutant EGFR and H1975 tumors) with TGI = 74.9 and 97.5% after oral administration (F = 27%), respectively. With an extraordinary kinome selectivity (S(10) score of 0.017), 52 undergoes detailed preclinical development.

Recent advances in total synthesis of natural products by masked ortho-benzoquinones
Chin. Chem. Soc. 2022, 69, 1210-1222.
The Diels-Alder adducts of maskedortho-benzoquinone (MOB) normally per-form high regio- and stereoselectivity and are generated under mild conditions.The advantages of MOB include: (a) Containing highly functional moieties:alkene, diene, carbonyl, enone, and dienone; (b) Easily accessible from2-methoxyphenol derivatives via oxidative dearomatization, and related2-methoxyphenol easily prepared from commercially available starting mate-rials; (c) The Diels-Alder adducts possessing unique features such as regio- andstereoselectivity and at least four contiguous stereogenic centers in one step.Furthermore, related bicyclo[2.2.2]octenone skeleton can be applied to furthercomplex structure construction by various chemical transformations, such asradical cyclization, oxa-di-π-methane rearrangement, Beckwith-Dowd rearran-gement, hydrogen atom transfer reaction, Cope rearrangement, Wanger-Meerwein rearrangement, carbonyl-ene reaction, aldol reaction, ring openingetc. Among these advantages, MOB system is prospected to continue as animportant intermediate for total synthesis of natural products

Natural product myricetin is a pan-KDM4 inhibitor which with poly lactic-coglycolic acid formulation effectively targets castration-resistant prostate cancer
J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 29.
Background: Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) with sustained androgen receptor (AR) signaling remains acritical clinical challenge, despite androgen depletion therapy. The Jumonji C-containing histone lysine demethylase
family 4 (KDM4) members, KDM4A‒KDM4C, serve as critical coactivators of AR to promote tumor growth in prostate
cancer and are candidate therapeutic targets to overcome AR mutations/alterations-mediated resistance in CRPC.
Methods: In this study, using a structure-based approach, we identifed a natural product, myricetin, able to block
the demethylation of histone 3 lysine 9 trimethylation by KDM4 members and evaluated its efects on CRPC. A
structure-based screening was employed to search for a natural product that inhibited KDM4B. Inhibition kinetics
of myricetin was determined. The cytotoxic efect of myricetin on various prostate cancer cells was evaluated. The
combined efect of myricetin with enzalutamide, a second-generation AR inhibitor toward C4-2B, a CRPC cell line, was
assessed. To improve bioavailability, myricetin encapsulated by poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), the US food and
drug administration (FDA)-approved material as drug carriers, was synthesized and its antitumor activity alone or with
enzalutamide was evaluated using in vivo C4-2B xenografts.
Results: Myricetin was identifed as a potent α-ketoglutarate-type inhibitor that blocks the demethylation activity by
KDM4s and signifcantly reduced the proliferation of both androgen-dependent (LNCaP) and androgen-independent
CRPC (CWR22Rv1 and C4-2B). A synergistic cytotoxic efect toward C4-2B was detected for the combination of myri‑
cetin and enzalutamide. PLGA-myricetin, enzalutamide, and the combined treatment showed signifcantly greater
antitumor activity than that of the control group in the C4-2B xenograft model. Tumor growth was signifcantly lower
for the combination treatment than for enzalutamide or myricetin treatment alone.Design and synthesis of novel orally selective and type II pan-TRK inhibitors to overcome mutations by property-driven optimization
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113673.
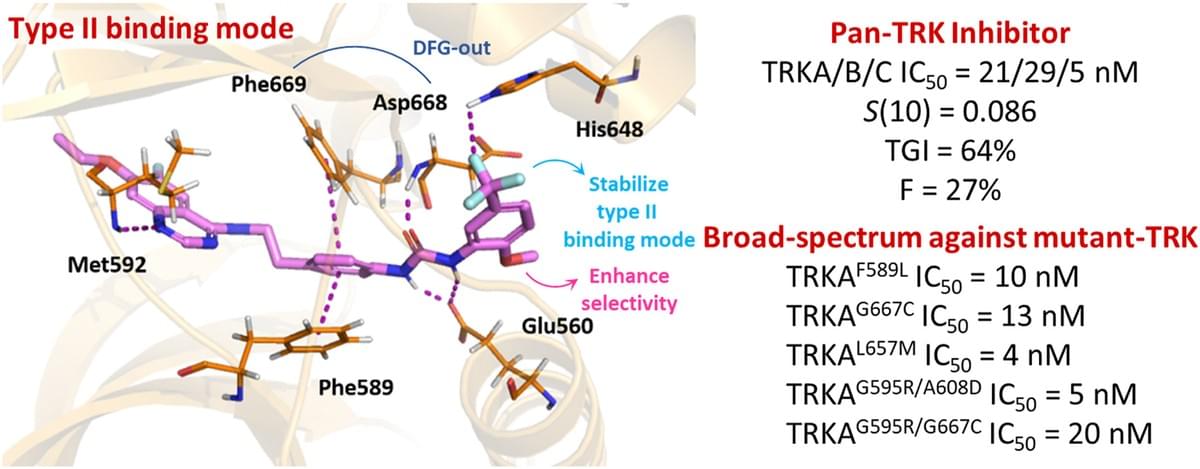
Rare oncogenic NTRK gene fusions result in uncontrolled TRK signaling leading to various adult and pediatric solid tumors. Based on the architecture of our multi-targeted clinical candidate BPR1K871 (10), we designed and synthesized a series of quinazoline compounds as selective and orally bioavailable type II TRK inhibitors. Property-driven and lead optimization strategies informed by structure-activity relationship studies led to the identification of 39, which showed higher (about 15-fold) selectivity for TRKA over AURA and AURB, as well as potent cellular activity (IC50 = 56.4 nM) against the KM12 human colorectal cancer cell line. 39 also displayed good AUC and oral bioavailability (F = 27%), excellent in vivo efficacy (TGI = 64%) in a KM12 xenograft model, and broad-spectrum anti-TRK mutant potency (IC50 = 3.74–151.4 nM), especially in the double-mutant TRKA enzymatic assays. 39 is therefore proposed for further development as a next-generation, selective, and orally-administered type II TRK inhibitor.
Discovery of BPR1R024, an Orally Active and Selective CSF1R Inhibitor that Exhibits Antitumor and Immunomodulatory Activity in a Murine Colon Tumor Model
J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 14477-14497
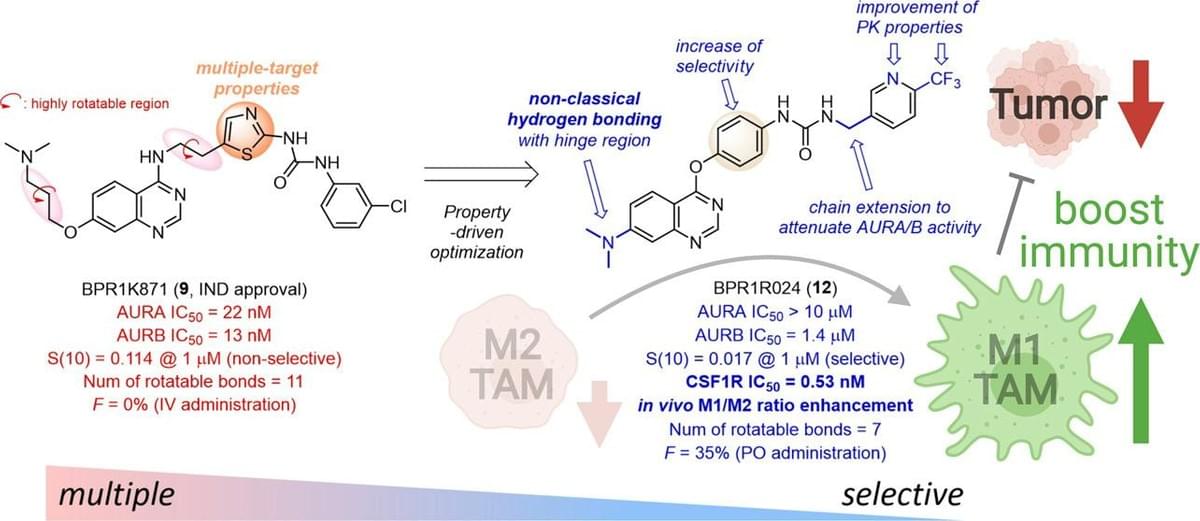
Colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF1R) is implicated in tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) repolarization and has emerged as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy. Herein, we describe the discovery of orally active and selective CSF1R inhibitors by property-driven optimization of BPR1K871 (9), our clinical multitargeting kinase inhibitor. Molecular docking revealed an additional nonclassical hydrogen-bonding (NCHB) interaction between the unique 7-aminoquinazoline scaffold and the CSF1R hinge region, contributing to CSF1R potency enhancement. Structural studies of CSF1R and Aurora kinase B (AURB) demonstrated the differences in their back pockets, which inspired the use of a chain extension strategy to diminish the AURA/B activities. A lead compound BPR1R024 (12) exhibited potent CSF1R activity (IC50 = 0.53 nM) and specifically inhibited protumor M2-like macrophage survival with a minimal effect on antitumor M1-like macrophage growth. In vivo, oral administration of 12 mesylate delayed the MC38 murine colon tumor growth and reversed the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment with the increased M1/M2 ratio.

Development of a Robust Scale-Up Synthetic Route for BPR1K871: A Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Solid Tumors
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2021, 25, 817–830.
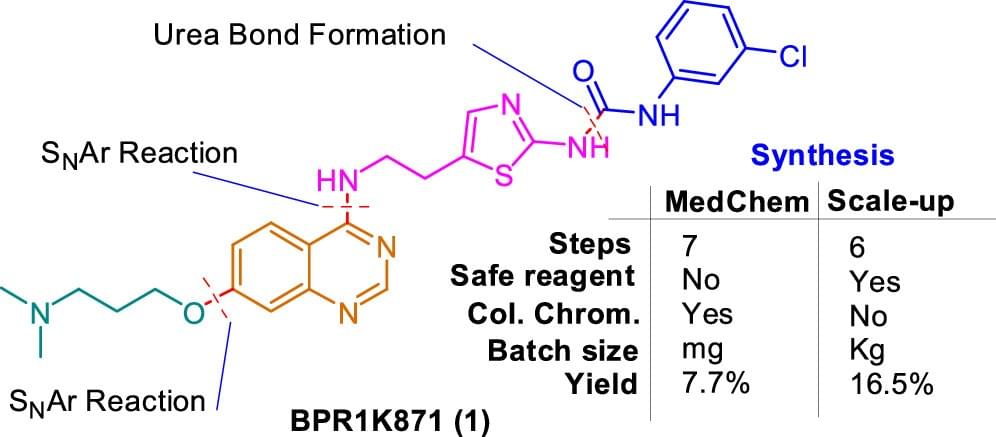
Herein, a robust and scalable procedure for the synthesis of multikinase inhibitor BPR1K871 (1, a quinazoline compound bearing a substituted thiazoline side chain), which is a clinical candidate for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and solid tumors, is reported. The previously reported medicinal chemistry synthetic route A with seven steps had encountered several issues during scale-up syntheses such as low yields (7.7% overall yield), the formation of inseparable impurities, particularly in the chlorination step, use of hazardous reagents (NaH/DMF), and laborious column chromatography steps for the purification of the products. A step-by-step approach to overcome the above issues was planned and implemented through two similar routes (B1 and B2) on a gram scale and finally through route B3 on a kilogram scale to synthesize 1. The final optimized synthetic route B3 does not require column chromatography purification steps. It is one step shorter than the original route A and avoided hazardous reagents for the alkylation reaction in step 2. Furthermore, the highlights of the new route B3 include liquid–liquid continuous extraction of compound 13 in step 2, the use of POCl3 instead of SOCl2 to minimize the formation of impurities in the chlorination step 3, and telescoped synthesis of key Boc-protected amino intermediate 15 from 13, in high purity. Using the scale-up route B3, the final product 1 (3.09 kg, yield of 16.5% over six steps with an HPLC purity of 97.8%) was obtained in a single batch for preclinical testing and facilitated clinical testing of 1, which is underway.

Tumor-agnostic inhibitors in oncology: A new phase forprecision medicine
Chin. Chem. Soc. 2021, 67, 2216-2224.
The study of precision medicine is flourishing in recent decades. Tumor-agnostic therapy is one of the targeted therapies, which can treat the malignant cellsregardless of where they grow. Herein we reviewed currently the U.S. FDAapproved tumor-agnostic therapies: one monoclonal antibody as a PD-1 inhibitor called pembrolizumab and four small-molecule kinase inhibitors,
larotrectinib, entrectinib, selpercatinib, and pralsetinib. We also summarized
the reported synthetic routes toward three drugs and some developing candidates under clinical trials as tumor-agnostic therapy.
Drug-like property optimization: Discovery of orally bioavailable quinazoline-based multi-targeted kinase inhibitors
Bioorg Chem. 2020, 98, 103689.
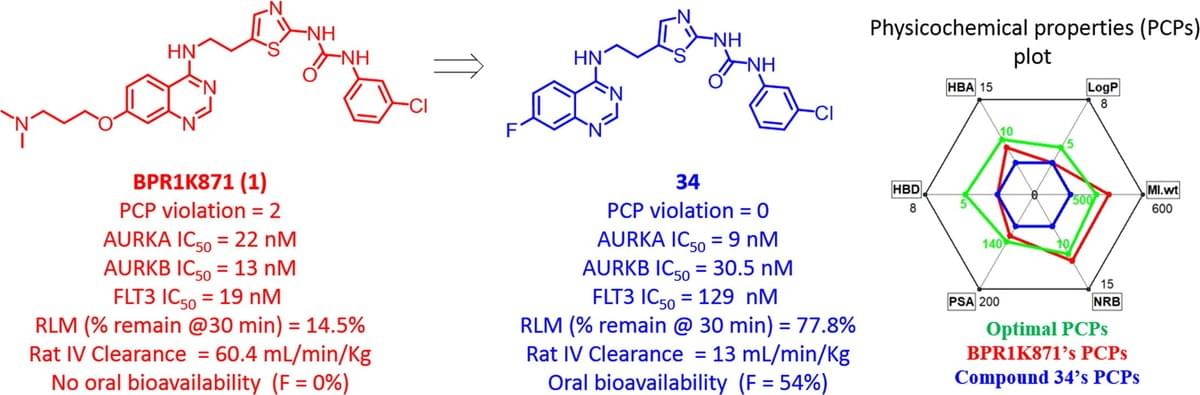
In an effort to develop new cancer therapeutics, we have reported clinical candidate BPR1K871 (1) as a potent anticancer compound in MOLM-13 and MV4-11 leukemia models, as well as in colorectal and pancreatic animal models. As BPR1K871 lacks oral bioavailability, we continued searching for orally bioavailable analogs through drug-like property optimization. We optimized both the physicochemical properties (PCP) as well as in vitro rat liver microsomal stability of 1, with concomitant monitoring of aurora kinase enzyme inhibition as well as cellular anti-proliferative activity in HCT-116 cell line. Structural modification at the 6- and 7-position of quinazoline core of 1 led to the identification of 34 as an orally bioavailable (F% = 54) multi-kinase inhibitor, which exhibits potent anti-proliferative activity against various cancer cell lines. Quinazoline 34 is selected as a promising oral lead candidate for further preclinical evaluation.

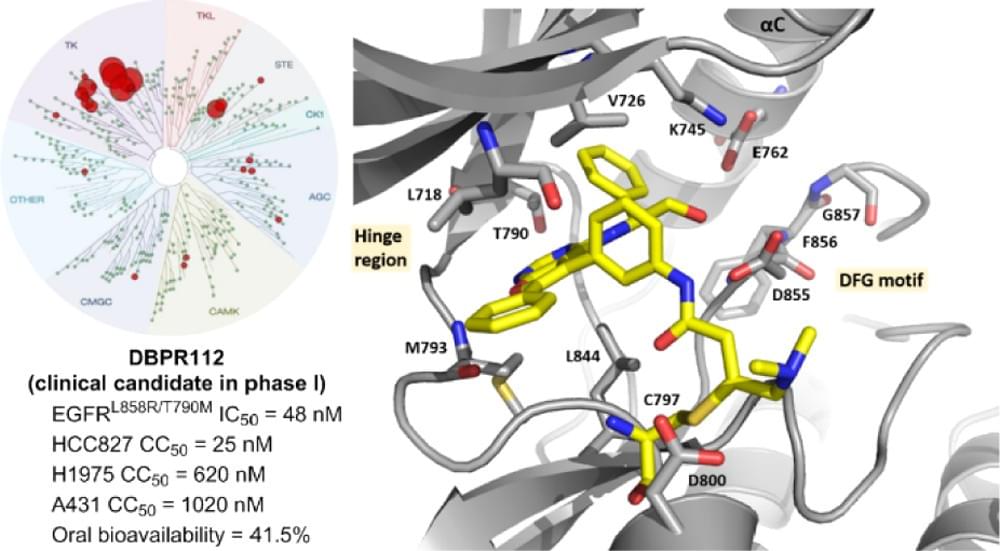
Discovery of a Furanopyrimidine-Based Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor (DBPR112) as a Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10108–10123
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer represents a breakthrough in the field of precision medicine. Previously, we have identified a lead compound, furanopyrimidine 2, which contains a (S)-2-phenylglycinol structure as a key fragment to inhibit EGFR. However, compound 2 showed high clearance and poor oral bioavailability in its pharmacokinetics studies. In this work, we optimized compound 2 by scaffold hopping and exploiting the potent inhibitory activity of various warhead groups to obtain a clinical candidate, 78 (DBPR112), which not only displayed a potent inhibitory activity against EGFRL858R/T790M double mutations but also exhibited tenfold potency better than the third-generation inhibitor, osimertinib, against EGFR and HER2 exon 20 insertion mutations. Overall, pharmacokinetic improvement through lead-to-candidate optimization yielded fourfold oral AUC better that afatinib along with F = 41.5%, an encouraging safety profile, and significant antitumor efficacy in in vivo xenograft models. DBPR112 is currently undergoing phase 1 clinical trial in Taiwan.

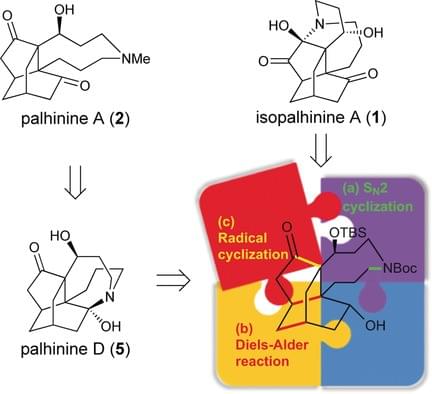
Biomimetic Syntheses of (±)-Isopalhinine A, (±)-Palhinine A, and (±)-Palhinine D
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15572–15576.
The first total synthesis of isopalhinine A, as well as unified syntheses of palhinine A and palhinine D, were successfully accomplished by means of a biomimetic strategy that proceeds through a bioinspired 5/6/6/9 tetracyclic intermediate, which mimics the amino ketone form of palhinine D. An early-stage direct SN 2 cyclization to construct the nine-membered azonane ring minimized the transannular strain that would otherwise be increased by the twisted nature of the isotwistane skeleton. Then, a diastereoselective Diels-Alder reaction of a masked ortho-benzoquinone using the nine-membered ring as a steric shielding group furnished a functionalized 6/6/9 tricyclic skeleton and established the desired stereochemistry at the C3, C7, C12, and C15 positions in one step. A thiol-mediated acyl radical cyclization gave the bioinspired intermediate bearing three differentiated oxygen-containing functional groups, from which all three total syntheses could be completed in either two or three additional steps.

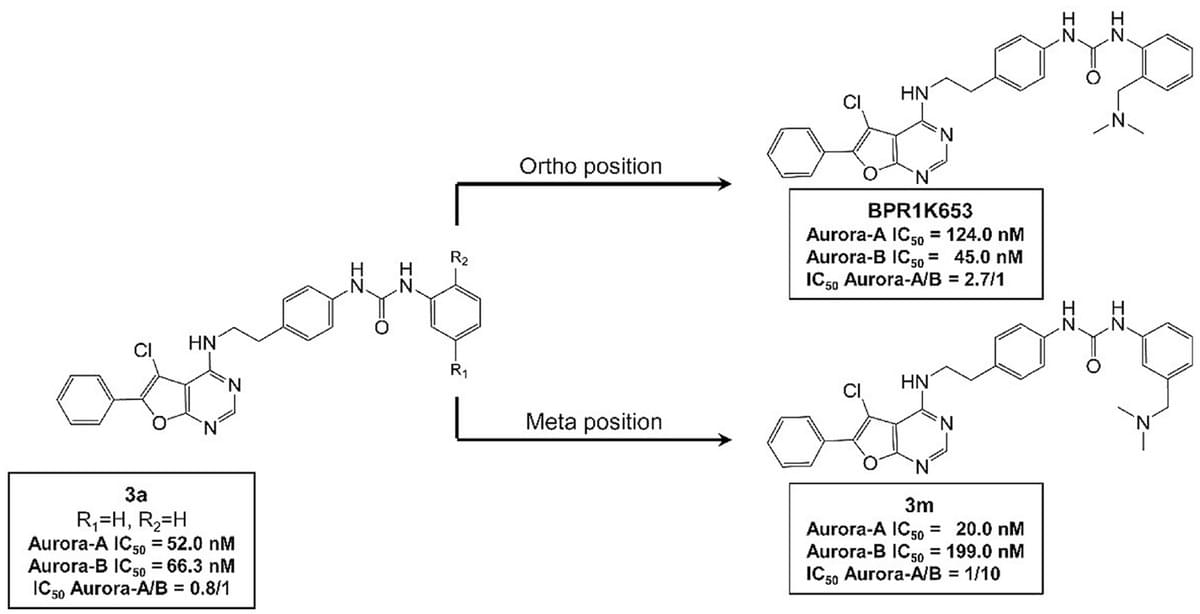
Design and synthesis of BPR1K653 derivatives targeting the back pocket of Aurora kinases for selective isoform inhibition
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 533-545.
Rare oncogenic NTRK gene fusions result in uncontrolled TRK signaling leading to various adult and pediatric solid tumors. Based on the architecture of our multi-targeted clinical candidate BPR1K871 (10), we designed and synthesized a series of quinazoline compounds as selective and orally bioavailable type II TRK inhibitors. Property-driven and lead optimization strategies informed by structure-activity relationship studies led to the identification of 39, which showed higher (about 15-fold) selectivity for TRKA over AURA and AURB, as well as potent cellular activity (IC50 = 56.4 nM) against the KM12 human colorectal cancer cell line. 39 also displayed good AUC and oral bioavailability (F = 27%), excellent in vivo efficacy (TGI = 64%) in a KM12 xenograft model, and broad-spectrum anti-TRK mutant potency (IC50 = 3.74–151.4 nM), especially in the double-mutant TRKA enzymatic assays. 39 is therefore proposed for further development as a next-generation, selective, and orally-administered type II TRK inhibitor.

Discovery of BPR1K871, a quinazoline based, multi-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of AML and solid tumors: Rational design, synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation
Oncotarget. 2016, 52, 86239–56.
The design and synthesis of a quinazoline-based, multi-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other malignancies is reported. Based on the previously reported furanopyrimidine 3, quinazoline core containing lead 4 was synthesized and found to impart dual FLT3/AURKA inhibition (IC50 = 127/5 nM), as well as improved physicochemical properties. A detailed structure-activity relationship study of the lead 4 allowed FLT3 and AURKA inhibition to be finely tuned, resulting in AURKA selective (5 and 7; 100-fold selective over FLT3), FLT3 selective (13; 30-fold selective over AURKA) and dual FLT3/AURKA selective (BPR1K871; IC50 = 19/22 nM) agents. BPR1K871 showed potent anti-proliferative activities in MOLM-13 and MV4-11 AML cells (EC50 ~ 5 nM). Moreover, kinase profiling and cell-line profiling revealed BPR1K871 to be a potential multi-kinase inhibitor. Functional studies using western blot and DNA content analysis in MV4-11 and HCT-116 cell lines revealed FLT3 and AURKA/B target modulation inside the cells. In vivo efficacy in AML xenograft models (MOLM-13 and MV4-11), as well as in solid tumor models (COLO205 and Mia-PaCa2), led to the selection of BPR1K871 as a preclinical development candidate for anti-cancer therapy. Further detailed studies could help to investigate the full potential of BPR1K871 as a multi-kinase inhibitor.

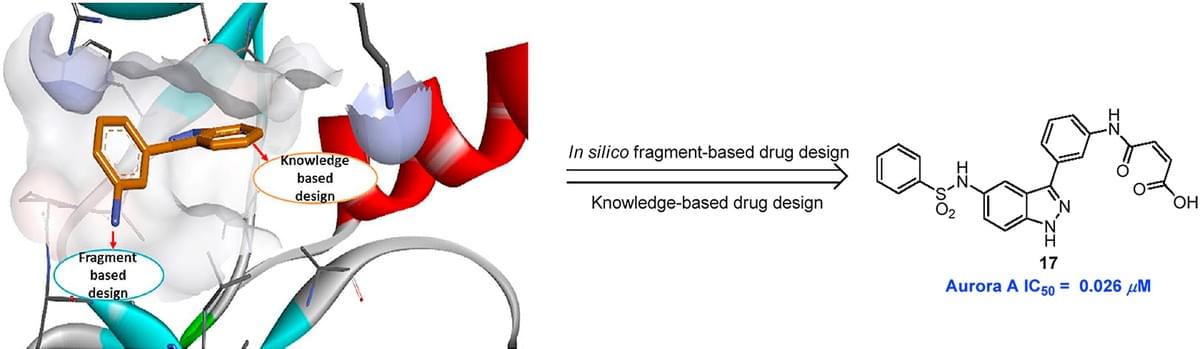
Discovery of novel inhibitors of Aurora kinases with indazole scaffold: In silico fragment-based and knowledge-based drug design
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 533-545.
Aurora kinases have emerged as important anticancer targets so that there are several inhibitors have advanced into clinical study. Herein, we identified novel indazole derivatives as potent Aurora kinases inhibitors by utilizing in silico fragment-based approach and knowledge-based drug design. After intensive hit-to-lead optimization, compounds 17 (dual Aurora A and B), 21 (Aurora B selective) and 30 (Aurora A selective) possessed indazole privileged scaffold with different substituents, which provide sub-type kinase selectivity. Computational modeling helps in understanding that the isoform selectivity could be targeted specific residue in the Aurora kinase binding pocket in particular targeting residues Arg220, Thr217 or Glu177.
© 2023